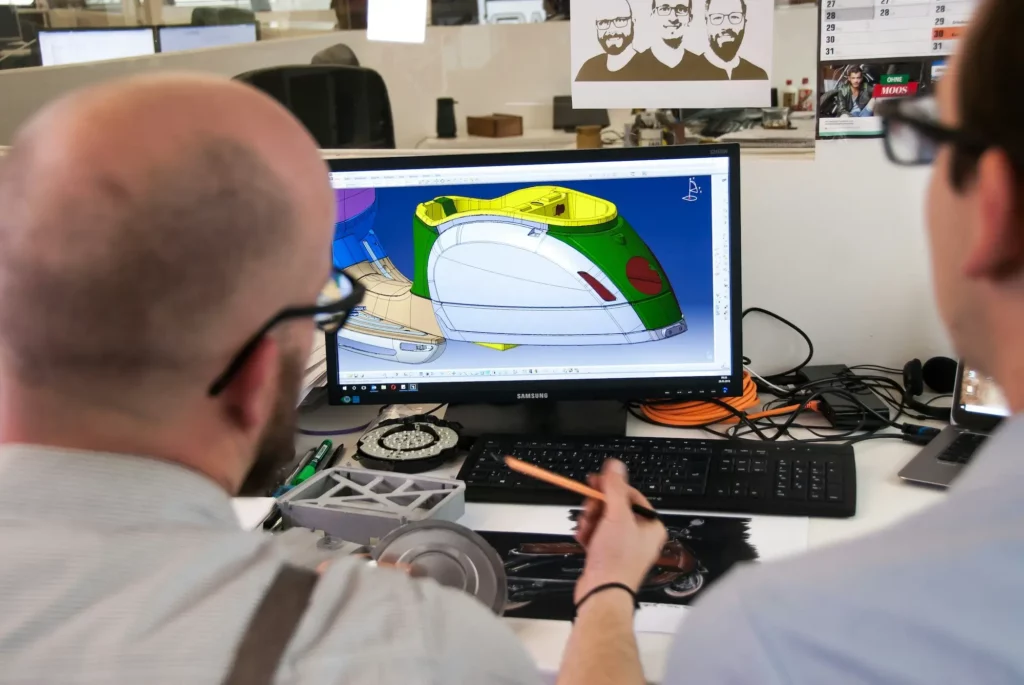
Mechanical engineering has always been about solving complex problems and turning ideas into real products.
Over the years, the tools used by engineers have shifted from paper drawings to advanced digital platforms that handle everything from design to simulation.
Today, the right software for mechanical engineers can speed up the design cycle, reduce errors, and make collaboration much smoother.
In this article, we’ll look at 10 mechanical engineering software options worth trying in 2025.
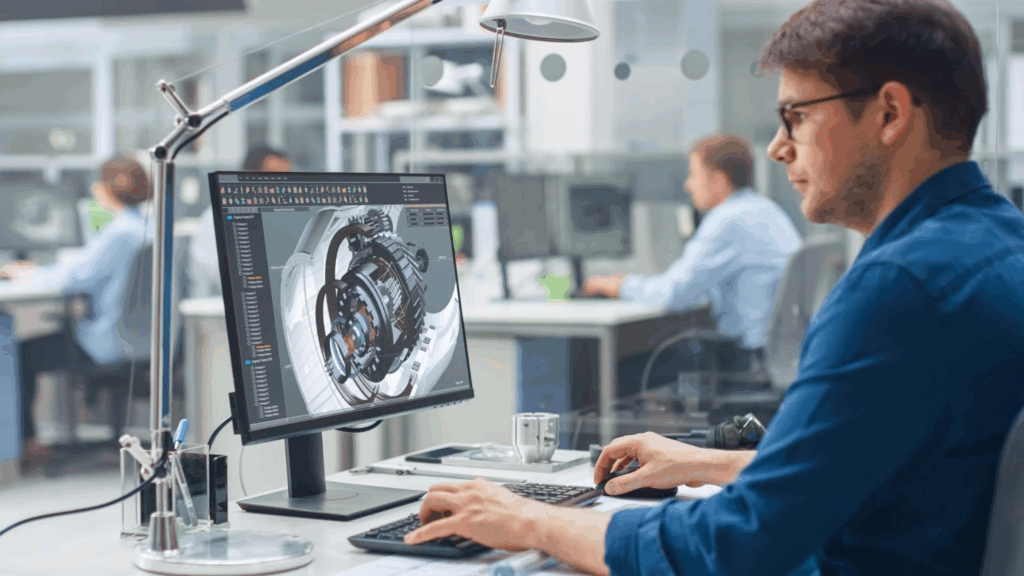

What is Mechanical Engineering Software?
Mechanical engineering software is a set of tools that engineers use to design, test, and improve machines. These programs help from the first sketch to the final product.
A common type is computer-aided design (CAD) software. It allows mechanical design engineers to create detailed 2D or 3D models that show how parts will look and fit together.
Other software for mechanical projects can run tests on stress, heat, or motion, giving teams a clear view of how a design will perform in real life.
With the right tools, mechanical design becomes faster and more accurate, while also reducing errors.
For product teams and designers, mechanical engineering software is a practical way to move from ideas to finished parts with confidence.
Book a demo now and see how CADchat simplifies design reviews for mechanical engineering teams.
Computer-Aided Engineering vs Computer-Aided Design: What’s the Difference?
When people talk about mechanical design software, they often hear both CAD and CAE mentioned together. While they work closely, they serve different roles.
Computer-aided design, or CAD, software creates digital 2D or 3D models. Engineers use it to shape products, set dimensions, and make technical drawings. These models guide design and are later used in manufacturing.
Computer-aided engineering (CAE) software tests those CAD models. With tools like finite element analysis, engineers can check stress, airflow, or heat before making prototypes.
This helps predict performance, improve energy use, and optimize shapes to cut material use while keeping strength.
Used across various industries, both CAD and CAE play important roles in modern mechanical design.
| Aspect | CAD | CAE |
| Main purpose | Creates 2D or 3D models with geometry and details | Validates designs through simulations |
| Outputs | Digital drawings and models | Simulation results like stress, heat, or motion |
| Process | Parametric modeling with construction history | Meshed models for calculations |
| Focus | Design creation and visualization | Product performance, testing, and optimization |
| Examples of use | Drafting parts for computer-aided manufacturing | Running finite element analysis software or topology optimization |
| Role in development | Helps build accurate geometry | Helps reduce physical prototypes and improve energy-efficient designs |
Tools for Easier CAD Collaboration
Working on designs is rarely a solo task. Mechanical engineers often need to share models, review changes, and work together on projects in real time.
Traditional methods like sending files back and forth or using screen share apps can slow things down and cause errors.
These tools help teams stay aligned, reduce mistakes, and move designs from idea to production with less friction.
1. CADchat
CADchat is a cloud-based platform built to make design review meetings and collaboration simple for product teams.
It combines real-time and asynchronous reviews in one place, so engineers, manufacturers, mechanical designers, suppliers, and non-technical stakeholders can work together without confusion.
With its intuitive user interface, CADchat removes the friction of file sharing and endless email chains. Teams can review 3D models live, leave comments tied directly to the design, and keep every version updated.
For organizations that want the best software to improve the CAD process, CADchat provides a clear space for faster decision-making, stronger supply chain collaboration, and smoother engineering design workflows.
Key Features
- Live CAD model reviews – Open, inspect, and annotate 3D CAD files in real time without screen sharing or file conversions
- Asynchronous collaboration – Leave feedback directly on models so distributed teams can review and respond at any time
- Persistent digital workspaces – Keep all files, comments, and decisions organized in one space to simplify the CAD process
- Engagement for all teams – Mechanical designers, engineers, and non-technical stakeholders can access and contribute easily through an intuitive user interface
- Smart version control – Works with all major CAD file formats to keep designs updated, tracked, and ready for supply chain management and engineering design decisions
- No installs required – Start sessions straight from a browser with secure cloud-based access, saving time for both technical and non-technical users
- Enterprise-grade security – Protect intellectual property with SOC 2 certification and strong encryption throughout the CAD process
2. CoLab Software
Source: colabsoftware.com
CoLab is a 3D collaboration platform that supports engineering teams during the review stage of the mechanical engineering design process.
It is built to help teams collect expert feedback, organize knowledge, and use AI tools to improve design checks.
Instead of treating reviews as a manual task, CoLab captures feedback in context, connects it with related data, and applies generative AI to automate routine steps.
The goal is to make the design process more consistent, traceable, and informed by past lessons.
Key Features
- Browser-based CAD access – Allows team members to explore models and give feedback without needing special CAD tools
- Structured feedback database – Saves comments with design context and organizes them for easy search and filtering
- Similarity engine – Connects new reviews with related designs and previous lessons learned to guide decisions
- AI-assisted reviews – Uses generative AI to check models and drawings against custom checklists for consistency
- Integration with PLM and CAD systems – Connects with tools like Windchill, Teamcenter, and 3DXPERIENCE while supporting over 30 CAD file types
3. Anark
Source: anark.com
Anark is a platform that supports model-based collaboration in engineering and manufacturing. It connects with existing CAD tools and PLM systems to make 3D data easier to share and understand.
The software focuses on creating digital product definition packages, which provide teams, suppliers, and customers with secure access to design information.
By simplifying publishing and collaboration, Anark helps reduce errors and improve traceability across the design and production process.
Key Features
- Model-based publishing – Transforms 3D CAD data into accessible formats like technical data packages, 3D PDFs, and collaboration spaces
- Integration with CAD and PLM systems – Connects with existing CAD tools and lifecycle management platforms for smoother workflows
- Technical data packages (TDPs) – Provides structured sets of information, including 3D models, 2D drawings, and bills of materials
- Data governance and compliance – Adds watermarks, labels, and markings to protect intellectual property and meet compliance requirements
- Work instruction creation – Uses engineering data to build visual work instructions and inspection plans linked to product definitions
Software Programs for Mechanical CAD Modeling
Choosing the right tool can make a big difference in how smoothly a project moves from concept to production.
Many engineers look for the best mechanical CAD software that not only supports precise modeling but also fits well into team workflows. Let’s look at three popular CAD software programs today.
1. AutoCAD
Source: autodesk.com
Autodesk AutoCAD is a computer software application used worldwide for 2D drafting and 3D modeling.
It is widely recognized as one of the most established mechanical CAD design software tools, supporting architects, engineers, and designers in creating accurate digital models.
AutoCAD includes advanced capabilities such as AI-assisted drafting, customizable workspaces, and automated tasks that help speed up the design process.
Key Features
- 2D and 3D modeling – Create and annotate geometry, solids, surfaces, and mesh objects for detailed designs
- AI-assisted tools – Automate drafting tasks such as comparing drawings, publishing layouts, and creating schedules
- Customizable workflows – Use AutoLISP, APIs, and apps to adapt the software to specific project needs
- Extensive library of toolsets – Access seven specialized toolsets, including mechanical, architectural, and electrical design packages
- Cloud-based collaboration – Work with DWG files across desktop, web, and mobile while managing design data with Autodesk Docs
2. CATIA
Source: 3ds.com
CATIA is a CAD software used in many industries for the full product development process. It goes beyond standard 3D design by bringing modeling and simulation together in one platform.
With its advanced tools, CATIA lets teams design, test, and improve mechanical, electrical, and fluid systems in a connected workflow.
It also supports systems engineering and model-based design, making it helpful for complex projects that combine hardware, software, and performance needs.
Key Features
- 3D design and styling – Tools for creating detailed product geometry, surfaces, and industrial design concepts
- Advanced modeling capabilities – Integrated modeling and simulation to support complex mechanical and mechatronic systems
- Systems engineering support – Model-based solutions for integrating mechanical, electrical, and software-driven components
- Collaborative environment – Web, mobile, and augmented reality features that connect global teams in shared design spaces
- Product development integration – End-to-end coverage of the product development process, from concept modeling to final validation
3. Fusion 360
Source: autodesk.com
Fusion 360 is another tool from Autodesk that combines CAD and CAM in a single environment, supporting the full product lifecycle from idea to manufacturing.
It is used by engineers, designers, and students to create and test products with precision while keeping workflows connected.
The software supports parametric modeling for detailed 3D design as well as simulation and prototyping. With built-in generative design tools, Fusion 360 helps reduce material use, cut costs, and optimize shapes for performance.
Key Features
- Parametric modeling – Create precise 3D models with adjustable parameters for easy design changes
- Generative design – Explore optimized shapes that reduce material use and improve efficiency
- Combines CAD and CAM – Integrates design and manufacturing workflows in one platform
- Cloud-based collaboration – Share projects and work with teams and stakeholders in real time
- Simulation tools – Run stress tests, motion studies, and thermal analysis directly on 3D models
CAE Tools for Simulations & Analysis
Designing a product is only the first step. Mechanical engineers also need to understand how a design will perform in real conditions.
CAE tools make this possible through simulations that test stress, airflow, and heat transfer without the need for physical prototypes. Here are two CAE tools commonly used by engineers.
1. Ansys

Source: ansys.com
Ansys is a simulation platform widely recognized as finite element analysis (FEA) software that also supports computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and multiphysics simulations.
Engineers and researchers use it to simulate real-world conditions, including structural mechanics, heat transfer, fluid flow, electromagnetism, and combined physical effects.
Ansys provides tools for geometry creation, meshing, solving, and post-processing within a single interface.
Key Features
- Multiphysics simulation – Models and analyzes combined effects of fluid flow, thermal transfer, structural mechanics, and electromagnetics
- High-fidelity modeling – Creates detailed geometries that closely reflect real-world designs for accurate simulations
- Extensive material database – Includes data for metals, composites, fluids, acoustics, and other materials
- Parametric optimization – Tests multiple design options under different conditions to find the most effective design
- Integration with CAD software – Imports CAD geometries directly for streamlined simulation workflows
2. Abaqus
Source: 3ds.com
Abaqus is a general-purpose finite element analysis software used in mechanical engineering and civil engineering to handle a broad range of simulation needs.
It is used in structural analysis, thermal studies, acoustics, mass diffusion, piezoelectricity, and electrochemistry.
With its extensive library of element types and material models, Abaqus can represent metals, polymers, reinforced concrete, ceramics, soil, rock, and more under varied conditions.
Key Features
- Structural analysis – Simulates stress, deformation, and failure across metals, composites, and geotechnical materials
- Extensive material library – Covers isotropic and anisotropic materials, polymers, concrete, ceramics, foams, and more
- Multiphysics simulation – Supports coupled studies of heat transfer, acoustics, piezoelectricity, and diffusion processes
- Modules for different needs – Includes Abaqus/Standard, Abaqus/Explicit, and Abaqus/CAE for specialized simulation workflows
- High-performance computing support – Runs large and complex models efficiently using advanced computing resources
Tools for Managing Design Projects
Mechanical design projects often involve many people, files, and tasks happening at the same time. Keeping everything organized can be a challenge without the right support.
Project management tools designed for engineers help teams track progress, share updates, and stay on schedule.
Here are two tools that can simplify project management for design teams.
1. Autodesk Vault
Source: autodesk.com
Autodesk Vault is a product data management (PDM) system designed to organize and control engineering information across teams.
It integrates with Autodesk design tools and other 3D CAD programs, providing a central location for files, version histories, and project data.
It also extends into product lifecycle management when paired with Fusion Manage, allowing organizations to manage change processes, bills of materials, and supplier collaboration.
Key Features
- Centralized data management – Keeps CAD files, AutoCAD drawings, and project information organized in a shared system
- Revision control – Tracks design history and changes, ensuring teams work with the most current version
- Integration with 3D CAD programs – Works seamlessly with Autodesk Inventor, AutoCAD, and other CAD tools
- Remote access options – Provides mobile and browser-based access through Vault Gateway and Project Sync
- Product lifecycle management integration – Extends to Fusion Manage for processes like change management, BOM handling, and supplier collaboration
2. Trello
Source: trello.com
Trello is a project management tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to organize tasks, ideas, and workflows.
It is used in areas like product design and manufacturing to assign tasks and track progress. Trello also works well for projects with large teams that need to stay aligned.
Its setup makes it easy for engineers and other stakeholders to manage both simple tasks and complex projects in one system.
Key Features
- Boards and cards – Organize projects into boards with individual cards to represent tasks or items in product design or manufacturing products
- Inbox capture – Collect tasks and ideas from different sources, including email and messaging apps, allowing engineers to manage all inputs in one place
- Calendar and planner view – Arrange tasks by deadlines or schedules to keep product design and large assemblies aligned with timelines
- Automation tools – Apply no-code automation to repetitive workflows and updates in the project management software
- Integrations – Connect Trello with external apps and services to extend functionality for managing product design and manufacturing products
Annotate Straight to Your 3D Mechanical Design with CADchat
Design reviews often lose momentum when feedback is scattered across emails, chats, or static screenshots. CADchat solves this by bringing every discussion, annotation, and file into a single platform.
Teams work directly inside the 3D model, keeping all comments tied to the geometry itself. This approach saves time, reduces errors, and helps teams focus on moving designs forward.
For engineers, manufacturers, and product teams, CADchat is more than a meeting tool. It has become a leading choice for cloud-based CAD design reviews, offering real-time and asynchronous feedback options.
Non-technical stakeholders can join in without needing CAD expertise, while technical teams can edit and annotate together in a shared space.
FAQs About Mechanical Engineering Software
What CAD software do most mechanical engineers use?
Most mechanical engineers use SolidWorks and AutoCAD since they are known for being powerful tools in design and modeling.
For team collaboration, CADchat is often the right fit because it helps engineers and product teams stay connected during the design process, especially when projects involve surface modeling or 3D CAD software.
Which software is used for CAD?
Several options are available for CAD, but the most common ones are AutoCAD, SolidWorks, CATIA, and Solid Edge. The choice depends on the industry, project needs, and whether the work involves simulation, drafting, surface modeling, or even additive manufacturing.
CADchat also supports collaboration for engineers and product teams, making it easier to link design work with the manufacturing process.
Do all mechanical engineers use SolidWorks?
Not all mechanical engineers use SolidWorks, though it is one of the most popular programs. Some engineers prefer AutoCAD, CATIA, or Solid Edge because different industries and companies choose different platforms for their design work.
Do I need Python for mechanical engineering?
Python isn’t required for every mechanical engineer, but it is helpful for tasks like automation, data analysis, and simulations.
With more engineers working on design optimization and additive manufacturing, knowing Python can give you an advantage in handling complex projects.


